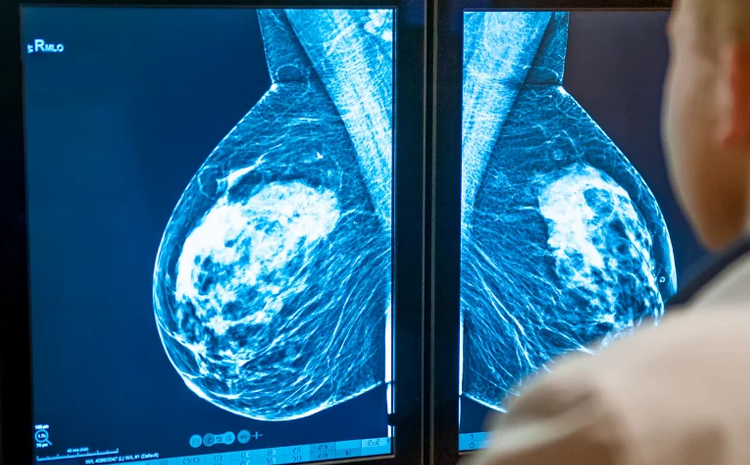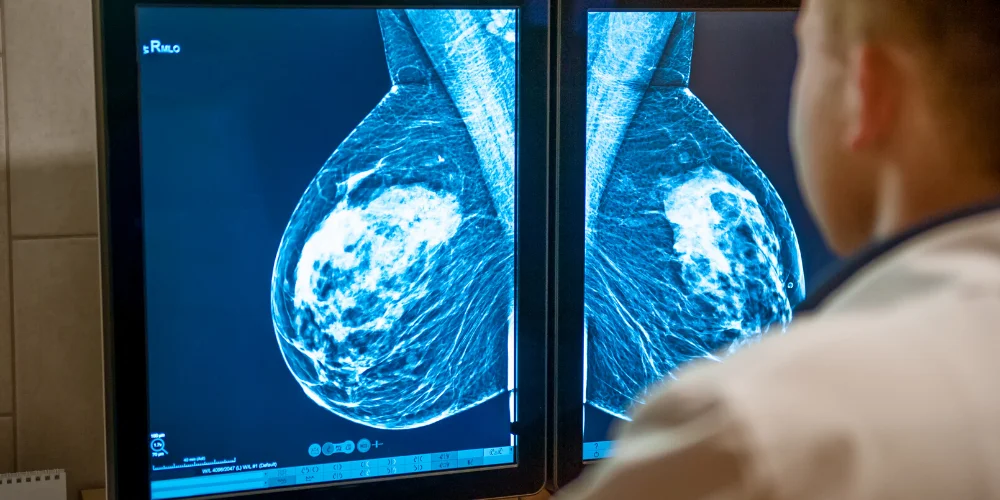
Digital Mammography
Mammography is a specialized medical imaging technique designed for the examination of breast tissue. It plays a crucial role in the early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer, which is one of the most common and potentially life-threatening forms of cancer among women.
Digital mammography uses electronic detectors to capture and store X-ray images digitally.
Advantages: Improved image quality, easier storage, and faster retrieval for analysis.
The primary goal of mammography is to detect abnormalities in breast tissue, such as tumors or cysts, at an early stage when they may not be palpable or visible through other means. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and increases overall survival rates.
Screening Mammography
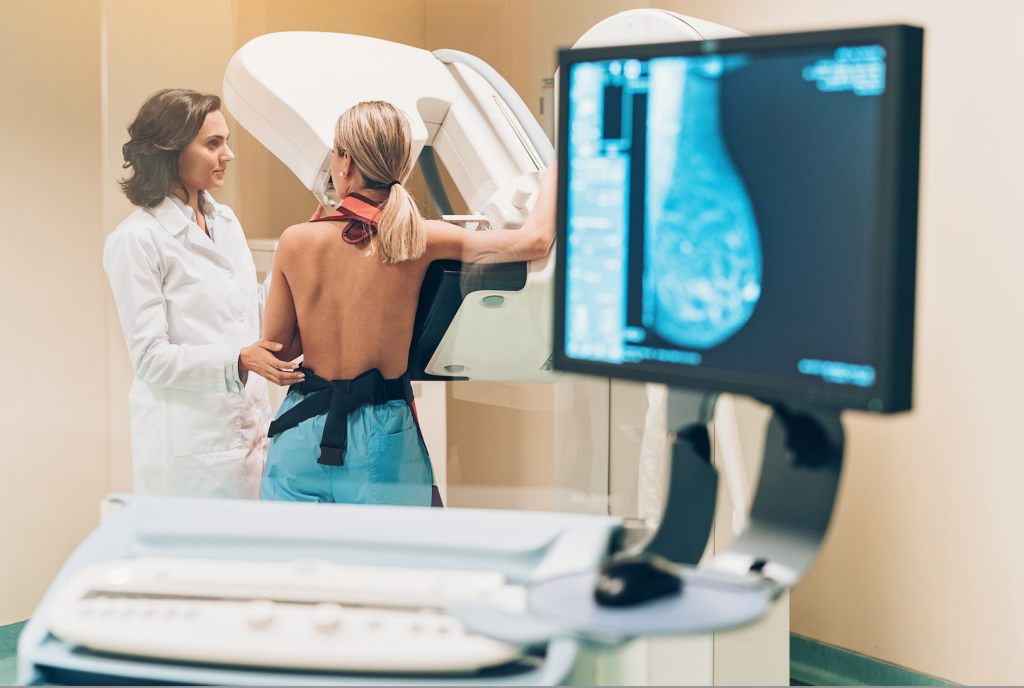
Purpose: To screen asymptomatic women for the early detection of breast cancer.
Frequency: Typically recommended for women of a certain age or with specific risk factors.
Procedure: Involves taking X-ray images (mammograms) of the breasts.
Diagnostic Mammography
Purpose: To investigate specific breast symptoms or abnormalities detected during screening.
Procedure: More detailed than screening mammography, with additional views and imaging techniques.
Mammography is a pivotal tool in the comprehensive approach to breast health, aiding in the timely detection and management of breast abnormalities. Advances in technology, such as digital mammography and tomosynthesis, continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of breast cancer detection, contributing to better outcomes for individuals undergoing screening and diagnostic evaluations.