Introduction to Interventional Radiology
Interventional Radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that utilizes imaging guidance to perform minimally invasive procedures for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Interventional radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in using advanced imaging techniques to visualize and treat various medical conditions without the need for traditional surgery.
Key aspects of Interventional Radiology include:
Imaging Modalities:
- Interventional radiologists use a range of imaging technologies such as fluoroscopy, ultrasound and CT (Computed Tomography) to guide their procedures in real-time.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- The hallmark of interventional radiology is its focus on minimally invasive techniques, which involve making small incisions or using natural body openings to access and treat targeted areas.
- These procedures often result in less pain, shorter recovery times, and reduced risk compared to traditional surgical approaches.
Therapeutic Interventions:
A significant aspect of interventional radiology involves therapeutic procedures aimed at treating a variety of conditions. Examples include:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Opening and supporting narrowed or blocked blood vessels.
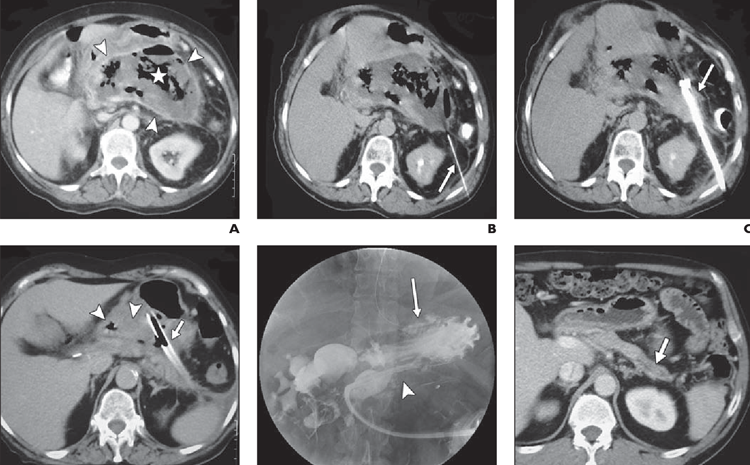
- Embolization: Blocking blood vessels to treat conditions such as bleeding or tumors.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Using heat to treat tumors or abnormal tissue.
- Catheter-based Therapies: Delivering treatments through thin tubes (catheters) guided by imaging.
Diagnostic Interventions:
- Interventional radiologists may perform diagnostic procedures to obtain tissue samples or assess the extent of a disease. Examples include biopsies and drainage procedures.
Vascular and Non-Vascular Interventions:
- Interventional radiologists may specialize in vascular interventions, dealing with blood vessels, or non-vascular interventions, addressing other organ systems.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
- Interventional radiologists often work closely with other medical specialists, surgeons, and healthcare teams to provide comprehensive care for patients.
Outpatient and Inpatient Settings:
- Many interventional radiology procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, reducing the need for hospitalization. However, some complex cases may require inpatient care.
Advancements in Technology:
- Ongoing technological advancements, such as robotic-assisted procedures and advanced imaging techniques, continue to expand the capabilities of interventional radiology.
Interventional Radiology plays a crucial role in modern medicine by offering less invasive alternatives to traditional surgery and providing innovative solutions for the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. The field continues to evolve, contributing to improved patient outcomes and expanded treatment options across a wide range of specialties